Project ScratchDuinoRobotKit blackline
From scratchduino
Name of author (s)
Description of the ROBBO Scratch project
| Trip time | Sketch | Power supply | ROBBO Scratch | Trip time | Arduino IDE |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| two extreme values, obtained when the sensor is positioned above the white area and above the black line. If the sensor shows a value greater than the average, then the robot turns to the left during 0.1 second and goes forward during 0.1 second. If the sensor shows a value less than the average, then the robot turns to the right during 0.1 second and goes forward during 0.1 second. The trajectory the robot follows is a zigzag.  | |||||
| 38 seconds | 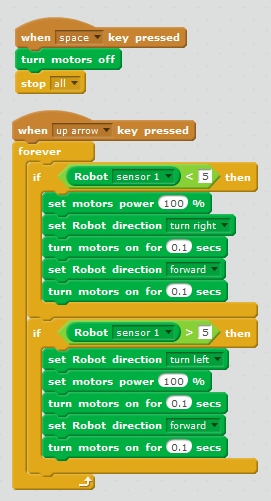
|
USB | ROBBO Scratch Video Download the sketch |
30 seconds | To turn the robot on and off, two touch sensors are used: analogRead(A3) – right-hand rear sensor — ON, analogRead(A1) — left-hand rear sensor — OFF Download the sketch |
| 13 seconds | The high speed causes numerous errors. At a high speed, the robot misses the turns in half the cases. |
Battery 7.4V | ROBBO Scratch Video Download the sketch |
11 seconds | Arduino IDE Video Download the sketch |
| two extreme values, obtained when the sensor is positioned above the white area and above the black line. The readings of the line sensor are as follows: » 1 means the position above the white area, closer to the black line. The left-hand motor is on and in full swing (255), rotating forward, while the right-hand motor is off. The robot turns on the fly during 0.1 second. » 2 means the position at the border of the white and black areas, even more closer to the black line. The left-hand motor is on and in full swing (255), rotating forward, while the right-hand motor is at its half power (120), rotating forward, too. The robot goes ahead and turns a bit, on the fly, during 0.1 second. » 3 means the position at the border of the white and black areas, already above the black line. The left-hand and the right-hand motors are on and in full swing (255), both rotating forward. The robot goes ahead during 0.1 second. » The rest of the values (4, 5, and 6) are mirroring the 0, 1, and 2 options, respectively. The trajectory the robot follows is a smooth curve with long tangent sections, so the robot can travel all along without slowing down.  | |||||
| 25–26 seconds | ROBBO Scratch handles the timing data with worse quality than Arduino IDE, therefore we have reduced the number of the ranges to 5 and simplified the action of motors. The motors are rotating forward all the time, with varying power. |
USB | Download the sketch | 18 seconds | Arduino IDE Video Download the sketch |
| 12 seconds | At a high speed, the robot misses the turn in 4 of 5 cases. |
Battery 7.4V | It is important to modify the sketch coded for USB, because at a high speed, the intermediate values of the sensor cannot be handled. We join all the intermediate values. Download the sketch |
9.5 seconds | It is important to immediately modify the sketch, coded for a 5V power supply (USB). Replace the robot's turning time of 0.1 seconds by 0.01 seconds. And increase the time of going ahead up to 0.2 seconds. It is necessary because at a high speed, the robot rushes too fast along the path section where the values of the sensors are changing. |
| is positioned above the white area and above the black line. The trajectory the robot follows is a line with long straight sections, and the robot can travel all along without slowing down.  | |||||
| XX seconds | |||||
| XX seconds | 8.5 seconds (track record!) | Arduino IDE Video Download the sketch | |||
Description of travelling along the black line with TWO sensors
When two sensors are used, special algorithms are needed to automate the robot's motion.
| Trip time | Sketch | Power supply | ROBBO Scratch | Trip time | Arduino IDE |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| that is, to the left and to the right from the black line. If both sensors are above the black line, the robot stops.  | |||||
| XX seconds | 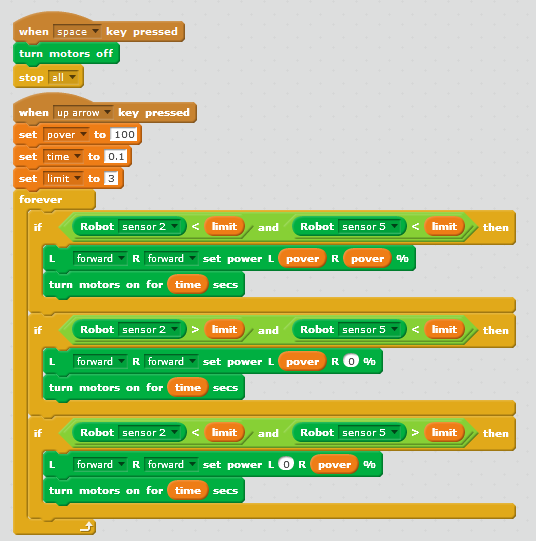
|
USB | When powered by USB, the robot stops at the turn, because both sensors get above the black line. Download the sketch | XX seconds |
analog0 = analogRead(A0); // Got a value from the sensor analog1 |
| 10 seconds | 7.4V | When extra powered from the battery, the robot misses the sharp turns, because at a speed, the sensors cannot be above the black line both at the same time. ROBBO Scratch Video Download the sketch |
XX seconds | [1] Arduino IDE Video]. If the battery charge is low, the robot stops at the turn. Download the sketch - sensor readings Download the sketch - relay controller + ON/OFF by touch sensors | |
| Such deflection is called error and we denote it with a letter E. In our case, the error is the difference between the readings of two line sensors: E = S1 – S2. To obtain the value of controlling action U, we multiply the E value by a chosen factor kp: U = kp⋅E. U is the momentum that we have to add to one motor and extract from other motor. Thus, the robot will control its position itself — that is, for turning or taxing to the required direction. | |||||
| USB | ROBBO Scratch Video | ||||
| XX seconds | Download the sketch | ||||
| 7.4V | [ROBBO Scratch Video Download the sketch] |
XX seconds | [Arduino IDE Video Download the sketch] | ||
| Algorithm 6. Proportional-plus-differential controller. | |||||
| USB | |||||
| 7.4V | [ROBBO Scratch Video Download the sketch] |
XX seconds | [Arduino IDE Video Download the sketch] | ||
| | |||||
| XX seconds | USB | ||||
| XX seconds | Battery 7.4V | [ROBBO Scratch Video Download the sketch] |
XX seconds | [Arduino IDE Video Download the sketch] | |